Rural Healthcare Transformation with Scalable Continuous Monitoring
Improve healthcare access, quality, and outcomes with BioIntelliSense's patient monitoring solution.
Core Technology
The BioButton wearable device continuous monitoring solution is designed for proactive patient monitoring, collecting and analyzing the leading indicators of patient decline.
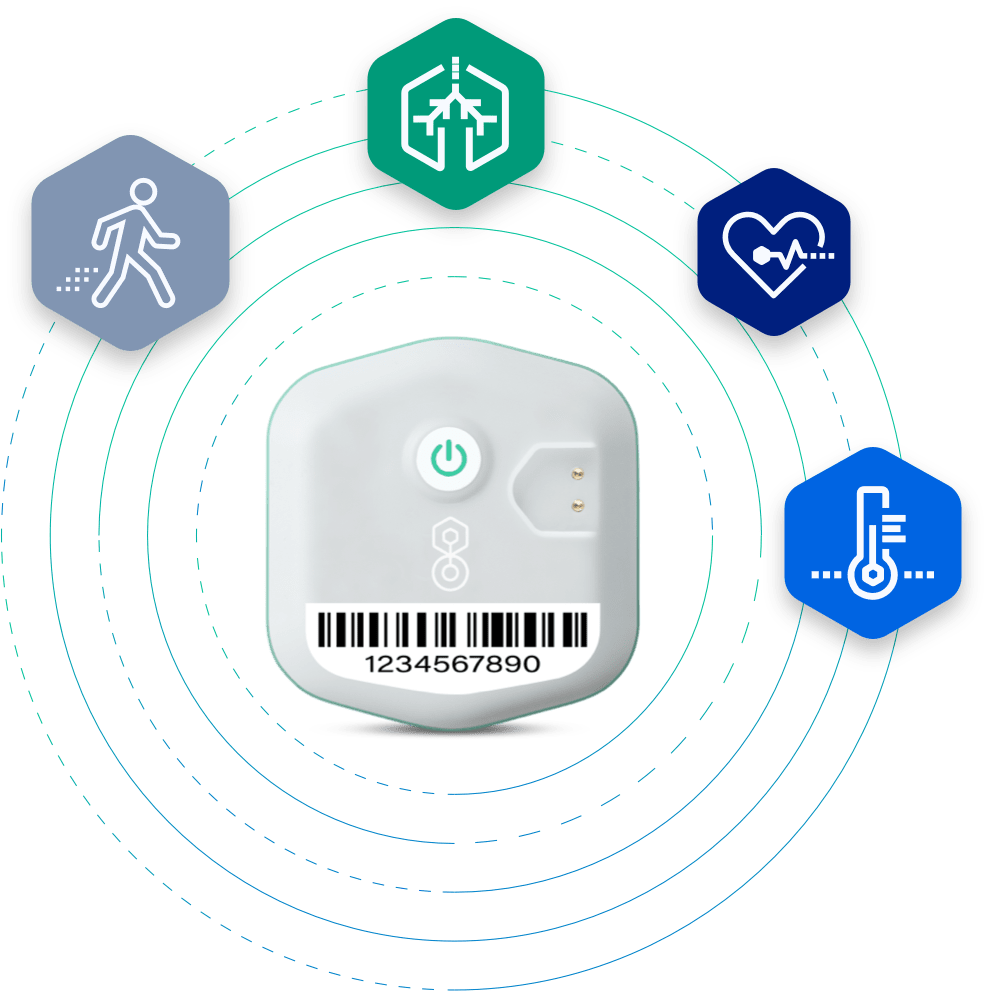
BioButton Wearable
Continuous vital sign and biometric measurements of patients both in facilities and at home
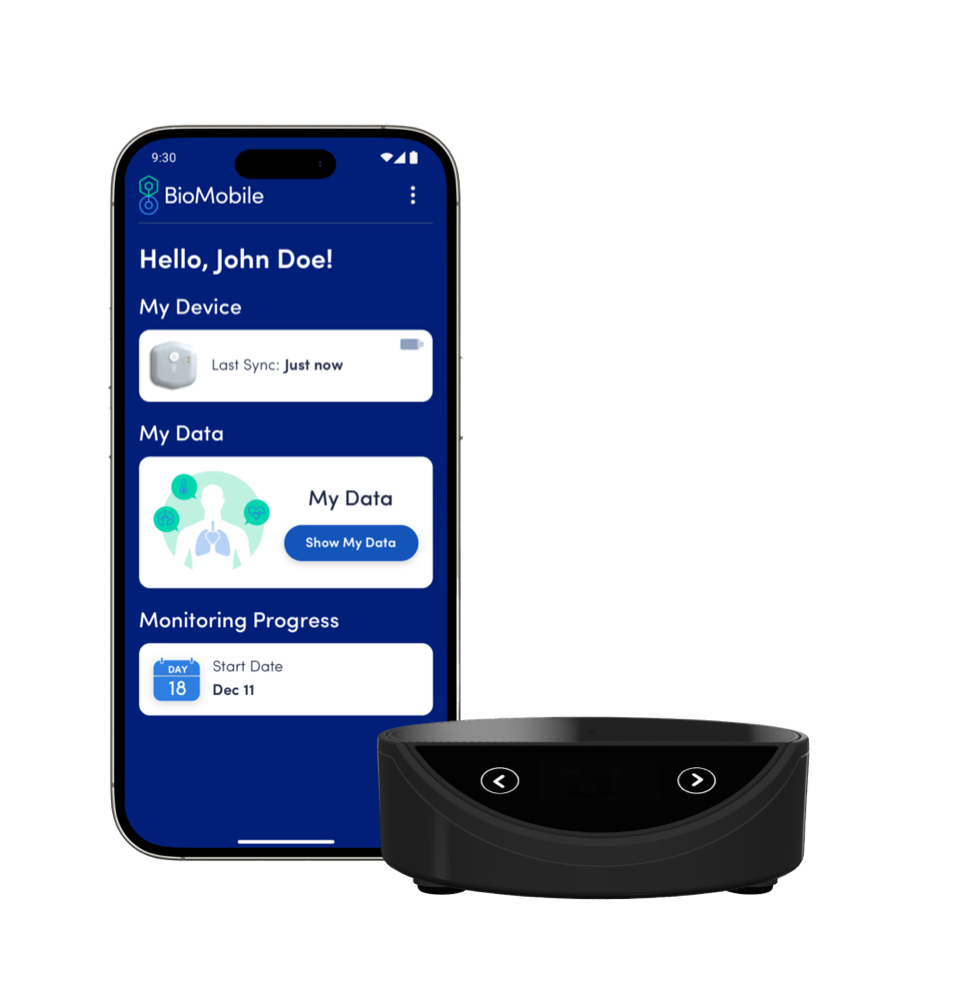
BioMobile Application
Patient-Facing Mobile App or BioHub Cellular Gateway
BioDashboard Display
AI-Exception Management Software to monitor patients in-hospital and/or home from a small office or command center
Rural Health Program Design
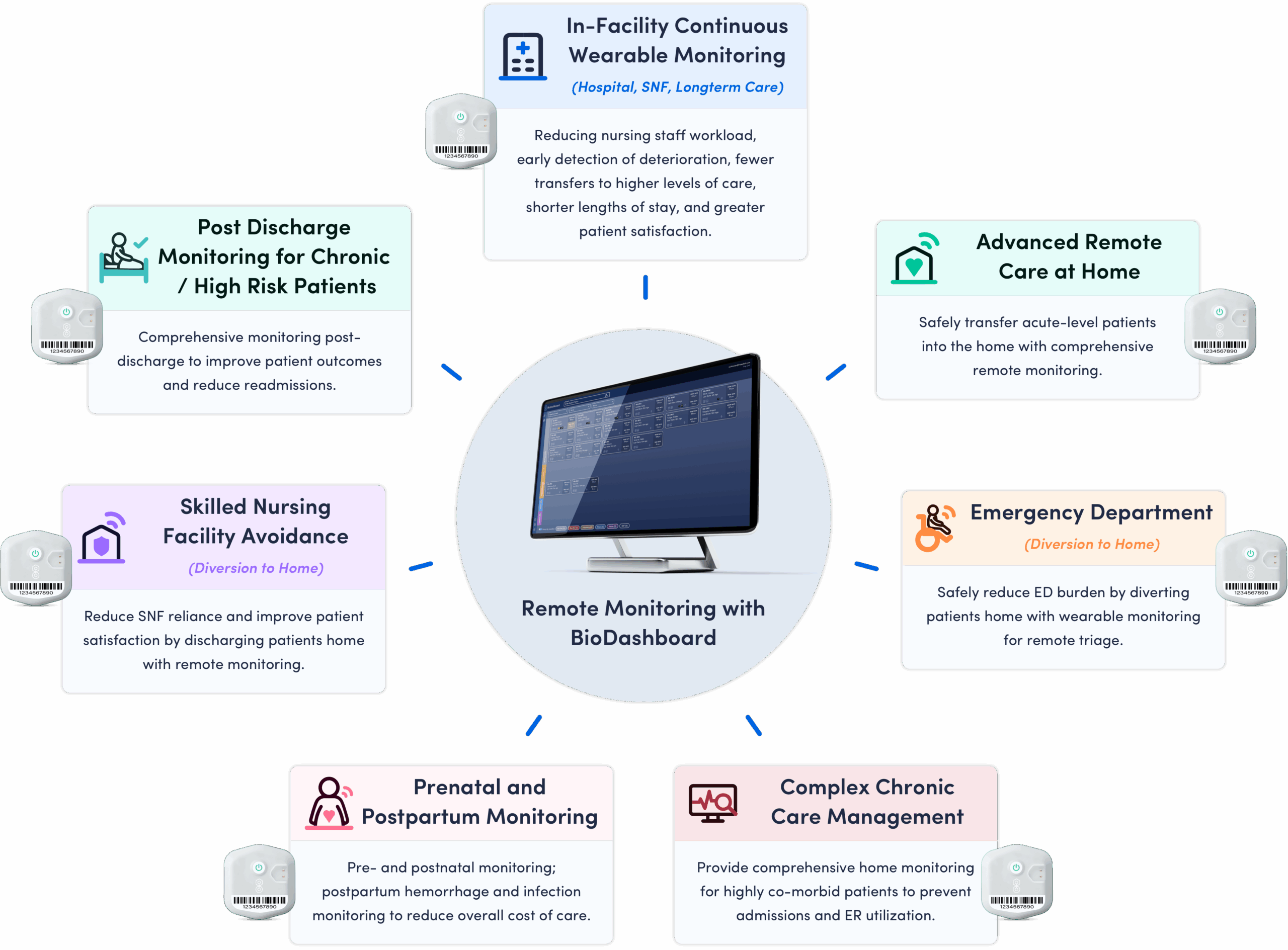
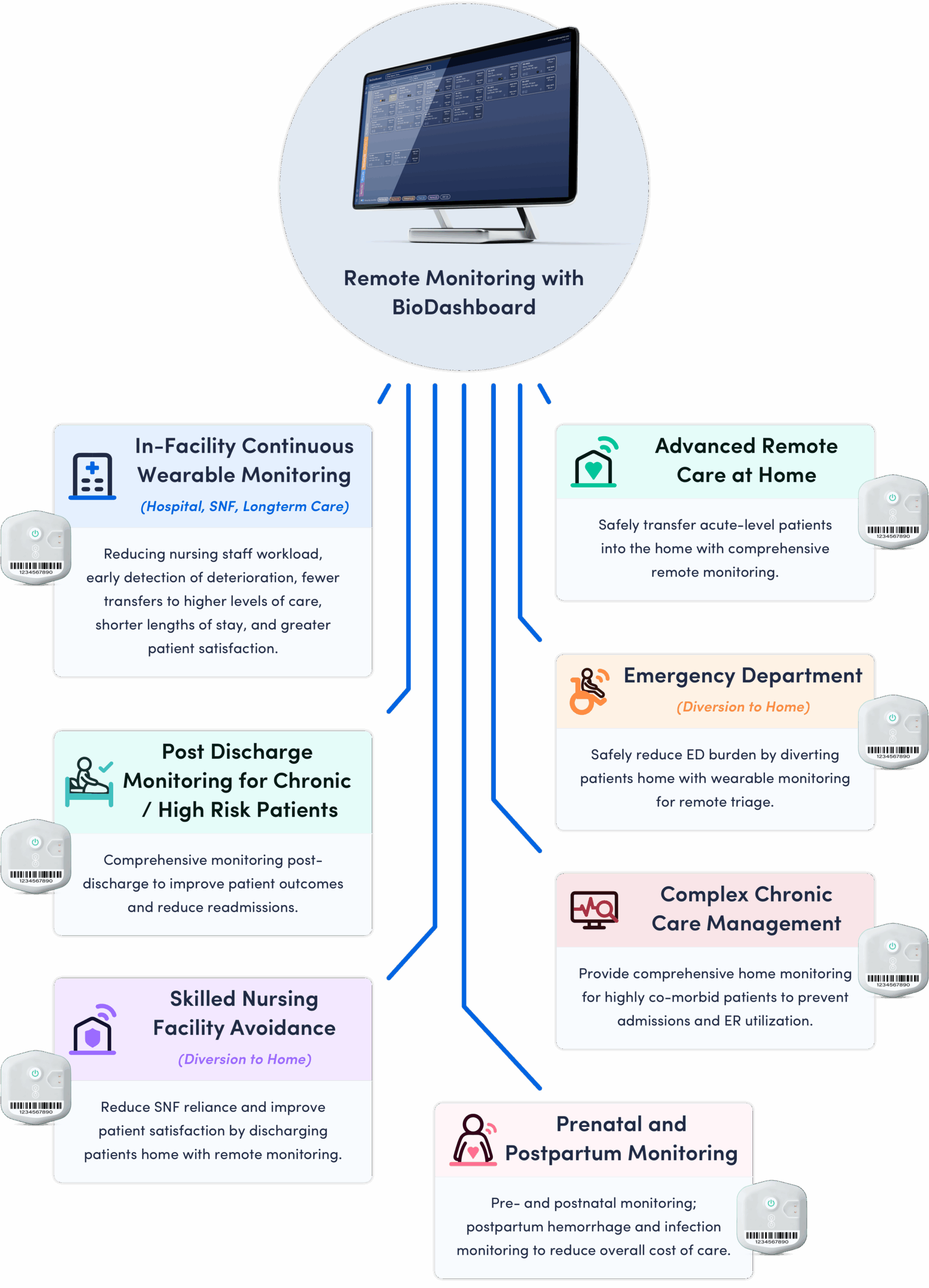
BioButton System Enables Multiple Remote Care Applications
Anticipated Impact on Health Outcomes, Access, and Quality
BioButton monitoring programs are used in diverse settings, enabling continuous monitoring and improving outcomes for non-ICU patients, whether in healthcare facilities or at home. Scalable and cost-effective, BioButton empowers rural hospitals to deliver high-quality care with greater efficiency and confidence.
Improved Health Outcomes
In-Facility
BioButton provides advanced notification of patients at risk for deterioration, which when compared to standard “spot-check” monitoring results in:
- Fewer transfers to higher level of care1-3
- Fewer rapid response team activations1,3,4
- Decreased length of stay5
At-Home: Post Acute and Chronic Care
BioButton provides comprehensive monitoring across a range of conditions in the period following discharge from the hospital, enabling:
- Reduction in hospital readmissions6
- Reduction in ER utilization6
- Improved management of Chronic Care Conditions7
Enhanced Access to Care
Remote wearable monitoring enables novel care models for rural communities, improving access to care by:
- Enabling remote primary care services with true insight into the patient’s health status
- Removing the need to travel to a facility to evaluate chronic condition symptomology
- Supporting earlier discharge from rural hospitals by allowing safe post-acute monitoring at home
- Centralizing monitoring resources so multiple rural facilities can access continuous oversight without duplicating staff
Improved Quality
The BioButton platform drives sustainable improvements in quality and efficiency by embedding continuous monitoring into standard workflows
Programs can enable and result in:
- Automation of repetitive, low impact work (manual vital work collection)
- Reduction in alert fatigue and burnout through personalized patient trending
- Data-driven patient care prioritization with nurse and providing facing tools
- Early detection of deterioration, preventing ER utilization and admissions
- Enhanced hospital IQR measures via reduced sleep interruption and improved patient restfulness
Together, these measures improve care quality, reduce alert fatigue, and boost staff satisfaction.

Request Our NOFO Proposal Kit
Ready to transform care for your patients? Use the form to request a copy of BioIntelliSense’s Rural Health Transformation Kit and learn how our solution can benefit your patients and healthcare professionals.
Tell us about yourself and we’ll take it from there!
For Remote Care Services Initiative
BioIntelliSense's FDA-Cleared Wearable Continuous AI Patient Monitoring System
An advanced technology solution that aligns with the eligible use of funds for Remote Care Services, meets factors evaluated within the technical scoring framework, and delivers outcomes.
Eligible Use of Funds
- Development of a standards-based platform that integrates and stores patient health data from remote monitoring devices and existing health records, enabling continuous monitoring both in facilities and at home, with AI-based clinical intelligence that delivers actionable information to providers and their patients.
- Training for digital health navigators, nurses, and/or community health workers to help patients learn to use these new technologies.
- Improving provider capacity to leverage continuous monitoring as a hub for managing both urgent and chronic conditions across care settings.
- Advancing data and clinical intelligence to improve outcomes: Demonstrating how AI-driven insights support proactive interventions and align with CMS’s focus on outcomes including decreased readmissions and emergency department use, improved management of chronic conditions, and increased patient satisfaction
- Building sustainable infrastructure: Offering clear financial models (per-bed/per-year and per-patient/per-episode) with extensive data collection/reporting that satisfy key RHT program technical factors.
Remote Care Services Outcomes
- Decreased rates of avoidable hospitalizations and readmissions.
- Decreased rates of avoidable emergency department use.
- Increased access to primary care.
- Increased access to specialty care, for example maternal fetal medicine providers.
- Improved management of chronic conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Reduce chronic disease progression in older adults.
- Increase patient satisfaction.
- Increase provider and patient digital literacy.
Applicable Technical Score Factors
| Technical Score Factor | Technical Score Factor Description | |
|---|---|---|
 |
B. 1. Population Health Clinical Infrastructure |
Four of the five leading causes of death in rural areas are associated with chronic disease. This situation is exacerbated by gaps in access to primary care and mental health services. Integrated care models may increase access to services in rural communities, as it is an effective strategy to maximize the use of scare rural health resources. Rural communities can benefit from integrated care models focused on preventative care, long-term care, behavior health, and other social health services through coordination amongst existing community stakeholders. |
 |
C. 1. Rural provider strategic partnerships |
Rural facilities face several challenges, including low patient volume and high fixed costs that lead to financial strain and workforce shortages that drive up labor costs and limit local resident access to primary and specialty providers. Rural health care facilities may choose to join clinically integrated networks with other rural facilities or partner with larger health care systems to share resources and improve access to services in their communities. These partnerships can improve the financial viability of rural providers through shared infrastructure and operations resources. Collaborations with a larger healthcare system may increase access to specialty services and promote sharing of best practices and training resources. |
 |
E. 1. Medicaid provider payment incentives |
Since its establishment in 2010, the CMS Innovation Center has been testing value-based care via its models. Outside of the Innovation Center, the concept of value-based care has existed since the late 1960’s. The concept rewards increases in quality and reductions in cost. Compared to urban residents, rural residents have a 44% higher rate of preventable ED visits and a 13% higher rate of preventable hospitalizations. Rural communities can benefit from participating in thoughtfully designed value-based programs focused on value over volume. States can consider leveraging learnings from the Innovation Center in designing these programs. |
 |
E. 2. Individuals dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid |
A larger share of Medicare beneficiaries in rural areas are covered by both Medicare and Medicaid than beneficiaries in urban areas. Although studies have found that beneficiaries enrolled in integrated care models have lower rates of hospitalization and readmissions than those who are not enrolled, a minority of dually eligible beneficiaries are now enrolled in integrated care, and there are fewer integrated care options available for dual eligible beneficiaries in rural areas. Dual-eligible beneficiaries in rural areas can benefit from more intentionally coordinated care for improved health outcomes and reduced total cost of care. |
 |
F. 1. Remote care services |
Rural areas often lack access to medical care due in part to distance from care and workforce shortages. Remote care services can help expand access to care by allowing clinicians of any type to provide rural residents with care from another location via telehealth, remote patient monitoring, or other modalities. While these services can be useful for rural residents, lack of Medicaid coverage for remote care services, lack of in-State providers, and limited infrastructure can all be limiting factors in providing remote care access for rural residents. |
 |
F. 2. Data infrastructure |
Rural geography and healthcare facility distribution often necessitate rural residents receiving care from providers and specialists outside of their community at different health systems. High-quality data infrastructure facilitating interoperability is vital for continuity of care. Data infrastructure can also improve rural health outcomes at a larger scale. IT software, for example, can allow hospitals to analyze their patient and outcome data on an aggregate level and make targeted improvements and clinical decisions. Similarly, high-quality T-MSIS data can help State and federal governments make informed decisions about rural healthcare needs. Despite their importance, rural hospitals have upgraded data infrastructure and facilitated patient access to health information at lower rates than other hospitals due to financial and human resources restrictions. |
 |
F. 3. Consumer-facing technology |
Consumer-facing health technology, such as symptom checkers and AI chatbots, are new developments which can help address critical rural healthcare access barriers like geographic isolation, high costs, and provider shortages. Tools like symptom checkers and virtual consultations enable rural patients to access care without traveling long distances by providing personalized health education and decision support. Providers can also leverage digital health tools to work more efficiently, lowering costs and mitigating provider shortages. |
See How BioIntelliSense Can Support Your Rural Health Transformation
Outcomes Reporting and Metrics
BioIntelliSense provides hospitals, community providers, and associated entities with easy-to-use dashboards that highlight patient utilization patterns, device performance, and key operational and facility quality metrics. All underlying data can be exported or configured into custom reports to meet site-specific needs. Recognizing the resource constraints many communities and rural facilities face, BioIntelliSense offers hands-on support to automate data collection, streamline reporting, and ensure insights are actionable. BioIntelliSense can also facilitate sharing of outcomes and program impact with health systems, state partners, and policymakers, fostering more informed engagement and decision-making.
Program Readiness
BioIntelliSense has developed a comprehensive framework to support rural health transformation, including implementation roadmaps, monitoring structure recommendations, standardized workflows, and economic planning resources. Hospitals partnering with BioIntelliSense gain access to scalable monitoring technology and analytic dashboards that strengthen operational efficiency and patient safety. With adequate program funding, BioButton monitoring and analytics can be deployed rapidly, with states able to stand up and begin monitoring patients within 6 months of funding.
Staffing & Training Plan
BioIntelliSense enables flexible staff models for setup, enrollment, and monitoring. The BioDashboard system can be deployed at any scale, from a single staff member to a full centralized command center. For both facility and home based programs, BioIntelliSense provides a robust suite of training materials and in-person training sessions for clinical staff. This includes dedicated sessions for select clinicians and staff with the customizable reporting dashboards and analytics tools.
Budget Approach
BioIntelliSense supports budgetary planning through its Rural Health Transformation Kit, which includes economic calculators to estimate technology, staffing, and operational costs based on facility size, patient volume, and program scope. This ensures that hospitals and policymakers can align resources with expected return on investment and sustainability goals. See section below for website link to request access to the kit.
Sustainability Plan
BioIntelliSense equips hospitals with the infrastructure and training to make continuous monitoring part of standard care. Programs are structured with cost-effective fees for rural facilities and supported by operational gains such as fewer readmissions, shorter lengths of stay, and the ability to expand into new service lines—creating a sustainable model that encourages broad adoption.
By embedding the BioButton into daily workflows, hospitals can achieve measurable reductions in overall cost of care improving outcomes. These efficiencies strengthen the financial foundation of rural facilities and position them to succeed in value-based care arrangements, including bundled payments and accountable care models. The result is long-term viability, demonstrated quality improvement, and alignment with both payers and policymakers.
Appendix A: Use of Funds Mapping Table
| # | Valid Uses of Funds | BioButton Enablement: |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Promoting evidence-based, measurable interventions to improve prevention and chronic disease management. |
The BioButton Monitoring System provides comprehensive monitoring for chronic disease patients during facility stay and following discharge from the hospital, enabling reduction in hospital admissions and ER utilization. |
2 |
Providing payments to health care providers for the provision of health care items or services, as specified by the Administrator. |
The BioButton Monitoring System is fully reimbursable under Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) codes, empowering providers to sustainably increase revenue and receive payment for tech-enabled care. This enables new care models, including but not limited to hospital-at-home and post-acute monitoring services; freeing up beds in rural facilities. |
3 |
Promoting consumer-facing, technology-driven solutions for the prevention and management of chronic diseases. |
Patients enrolled in BioButton Post-Acute monitoring are provided a comprehensive view of their health trends through the BioMobile application. Patients can share their personal health insights with their care team through exportable BioReports. |
4 |
Providing training and technical assistance for the development and adoption of technology-enabled solutions that improve care delivery in rural hospitals, including remote monitoring, robotics, artificial intelligence, and other advanced technologies. |
BioIntelliSense provides robust training and support to each facility it works with, ensuring each hospital achieves full adoption of continuous monitoring technology for all non-critical care patients. This includes support for onsite setup of networking, nurse and technician training for device management, as well as provisioning and training on how to leverage operational and clinical insights within the BioAnalytics platform. |
5 |
Recruiting and retaining clinical workforce talent to rural areas, with commitments to serve rural communities for a minimum of 5 years. |
BioIntelliSense supports programs for talent retention through:
|
6 |
Providing technical assistance, software, and hardware for significant information technology advances designed to improve efficiency, enhance cybersecurity capability development, and improve patient health outcomes. |
The BioButton monitoring system is purpose built to improve patient safety and health outcomes within the facility and the home. Including but not limited to:
These outcomes are possible by providing scalable continuous monitoring that transitions seamlessly from the hospital into the home. The BioButton also integrates seamlessly into the EMR and improves workflow efficiency through enabling effective patient prioritization. |
7 |
Assisting rural communities to right size their health care delivery systems by identifying needed preventative, ambulatory, pre-hospital, emergency, acute inpatient care, outpatient care, and post-acute care service lines. |
The BioButton monitoring system improves patient flow within the facility and enables providers to redirect utilization following patient discharge. Patients are monitored from (or before) admission, through their hospital stay, and into the home for 30+ days post discharge. |
8 |
Developing projects that support innovative models of care that include value-based care arrangements and alternative payment models, as appropriate. |
The BioButton monitoring system enables hospitals to implement innovative, value-based care models by reducing readmissions, shortening length of stay, and lowering overall costs. Continuous data and automated insights help identify at-risk patients earlier, empowering proactive interventions that align with accountable care and bundled payment programs. |
9 |
Additional uses designed to promote sustainable access to high quality rural health care services, as determined by the Administrator. |
The BioButton platform drives sustainable improvements in quality and efficiency by embedding continuous monitoring into standard workflows. This reduces the need for costly interventions, optimizes resource allocation, and ensures programs remain sustainable over time. Hospitals benefit from measurable cost reductions, improved patient safety, and the ability to scale best practices across service lines. |
Note – the only valid use of funds noted in the RHT Program that the BioButton monitoring system does not explicitly support:
Supporting access to opioid use disorder treatment services (as defined in section 1861(jjj)(1)), other substance use disorder treatment services, and mental health services.
Appendix B: Works Cited
- Eddahchouri Y, Peelen RV, Koeneman M, Touw HRW, van Goor H, Bredie SJH. Effect of continuous wireless vital sign monitoring on unplanned ICU admissions and rapid response team calls: a before-and-after study. Br J Anaesth. 2022;128(5):857-863.
- Verrillo SC, Cvach M, Hudson KW, Winters BD. Using Continuous Vital Sign Monitoring to Detect Early Deterioration in Adult Postoperative Inpatients. J Nurs Care Qual. 2019;34(2):107-113.
- Weller RS, Foard KL, Harwood TN. Evaluation of a wireless, portable, wearable multi-parameter vital signs monitor in hospitalized neurological and neurosurgical patients. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018;32(5):945-951
- Stellpflug C, Pierson L, Roloff D, et al. Continuous physiological monitoring improves patient outcomes. Am J Nurs. 2021;121(4):40–46.
- Sun L, Joshi M, Khan SN, Ashrafian H, Darzi A. Clinical impact of multiparameter continuous non-invasive monitoring in hospital wards: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J R Soc Med. 2020;113(6):217-224.
- Pedone C, Chiurco D, Scarlata S, Incalzi RA. Efficacy of multiparametric telemonitoring on respiratory outcomes in elderly people with COPD: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(82).
- Vudathaneni VKP, Lanke RB, Mudaliyar MC, Movva KV, Kalluri LM, Boyapati R. The impact of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring on healthcare delivery: A comprehensive evaluation. PMC. 2024;16(3):e55534.
COM-18451 Ver.0 | Published 2025-9